Minoxidil and its popular brand-name topical product, Rogaine, is a mainstay in reversing hair loss due to androgenetic alopecia in both men and women. In addition to a topical minoxidil lotion and foam, which are both available over the counter, a prescription oral form of minoxidil is also available.
Oral and topical minoxidil have been used for decades. According to clinical trial data, both forms of the medication were found to be safe and effective.
Table of Contents
How Minoxidil Works
Minoxidil takes about four months to have its full effect. Its exact mechanism of action is unknown, but science supports the idea that minoxidil works through several pathways.1,2
- Vasodilation: Minoxidil dilates blood vessels and increases blood flow to the hair follicle. This may promote hair growth by increasing the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to hair follicles.
- Extend the anagen phase: Minoxidil may extend the anagen growth phase in the hair growth cycle, which allows for longer, thicker hair.
- Opens ion gates in the hair follicle: Minoxidil may open potassium gates, causing increased hair growth early in the hair cycle.
- Increase vascular endothelial growth factors: Minoxidil may increase vascular endothelial growth factors, which extends the growth phase of the hair growth cycle.
Minoxidil topical solution and foam act locally. Topical minoxidil tends to have fewer side effects than oral minoxidil. It is well tolerated, but its effectiveness varies widely among individuals.

Oral Minoxidil
Oral minoxidil was initially intended to treat high blood pressure because it dilates or widens blood vessels. This decreases resistance in blood vessels, which reduces pressure. Hair growth was a noted side effect attributed to increased blood flow to the skin and hair follicles.
Oral minoxidil is available by prescription only. Topical minoxidil only promotes hair growth on the skin areas you apply it to. Oral minoxidil can encourage hair growth on the face and body.
Oral Minoxidil Side Effects
According to drugs.com, oral minoxidil is associated with the following side effects:
- Breast tenderness
- Chest pain
- Confusion
- Dizziness
- Fast heartbeat
- Flushing
- Headache
- Lightheadedness
- Nausea
- Rapid weight gain from fluid retention
- Skin rashes
- Swelling in the hands and feet
- Unwanted excess facial hair growth
- Vision changes
- Vomiting
Hypertrichosis, or excessive hair growth, is the most common side effect (20% of patients) associated with oral minoxidil. It appears to be dose-related.3
Side effects and effectiveness may be used to titrate the dosage. This list of potential side effects is not complete. See the manufacturer’s patient information page for more information.

Topical Minoxidil
Topical minoxidil works in the same manner as oral minoxidil pills, but because it is applied locally, it has a lower incidence of systemic side effects. The exact mechanism of action is unknown, but it is believed to lengthen the hair follicle growth cycle, causing an increase in hair follicle diameter and length.3
Topical minoxidil comes in a 2% and 5% solution and a 5% foam.
Topical Minoxidil Side Effects
The common side effects associated with minoxidil include scalp itching, scalp scaling, excessive hair growth, and changes in hair color and texture.
The following minoxidil side effects are rare but more serious:
- Severe scalp irritation
- Unwanted excessive facial hair growth
- Chest pain
- Fast heartbeat
- Swelling in the hands and feet
- Rapid weight gain from fluid retention
- Lightheadedness
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Confusion
- Flushing
- Vision changes
Because minoxidil changes the length of the growth and resting phases in the hair follicle growth cycle, many people experience minoxidil hair shedding in the first few weeks of treatment. This is expected based on how minoxidil topical works. It is important to be aware of this adverse effect so minoxidil is not stopped prematurely.
Which Type of Minoxidil Is Best for Hair Loss?
Oral minoxidil may work better for people with androgenetic alopecia, but it can potentially cause more serious side effects. Researchers looked at how well a 5% minoxidil solution applied to the scalp compared to taking 1 mg of minoxidil by mouth to treat female-pattern hair loss. They found that both forms of minoxidil worked equally well. Oral minoxidil had a safe medication profile and well-tolerated adverse events.4
Many people try topical minoxidil products first because they are available over the counter.
Which Type of Minoxidil Is Safest to Take?
After reviewing the literature, researchers found that low-dose oral minoxidil is a safe and effective treatment for hair loss. The most common side effect noted was excess, unwanted hair growth. Because oral minoxidil dilates blood vessels and lowers blood pressure, dizziness or fainting when standing can occur. Talk to your doctor about using the lowest effective dose of oral minoxidil to minimize the side effects.
If you have heart disease, high blood pressure, or chest pain, talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of using minoxidil.
Alternatives to Topical and Oral Minoxidil
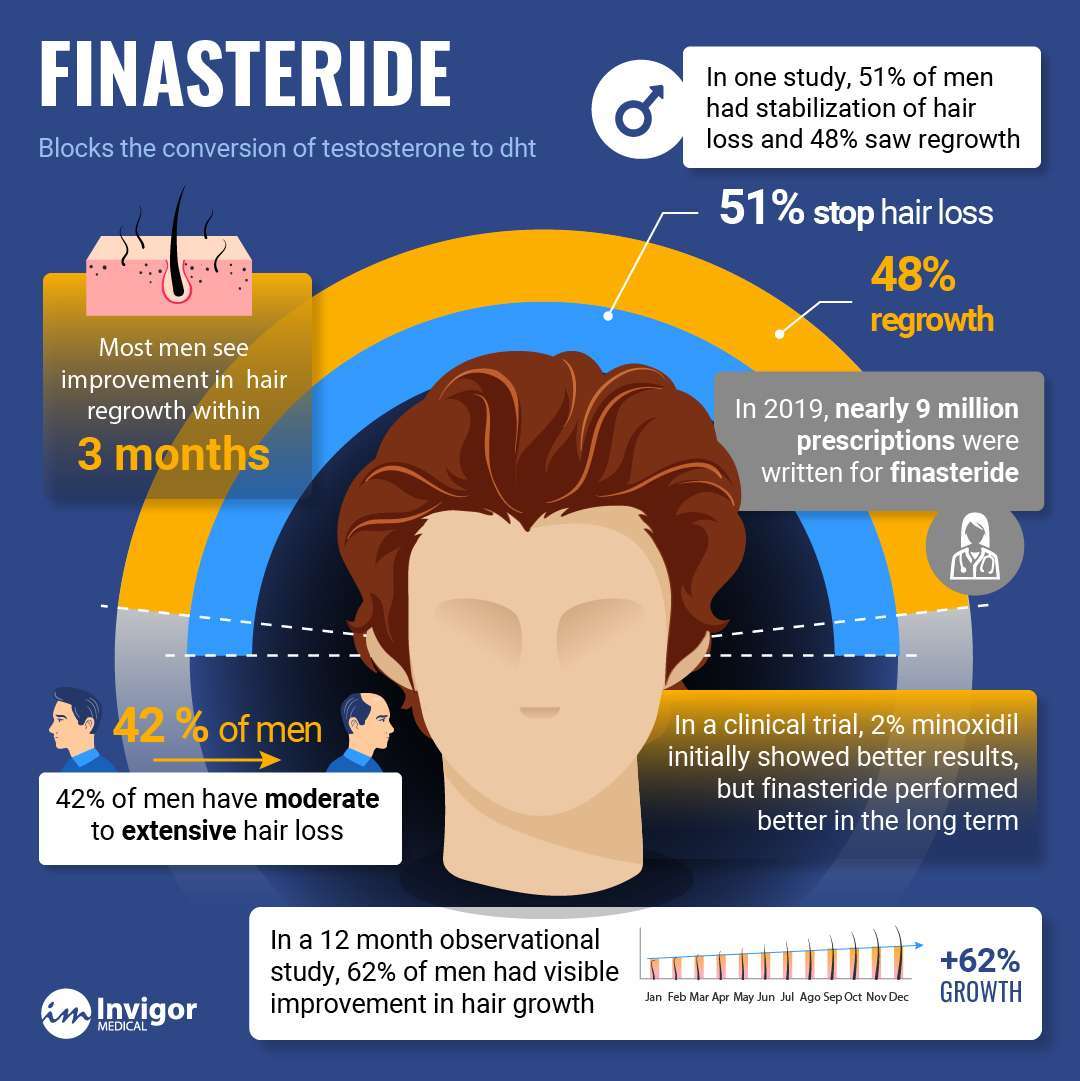
Finasteride is the other commonly prescribed medication to reverse and treat hair loss. Finasteride acts in the testosterone-dihydrotestosterone (DHT) pathway. It decreases the conversion of testosterone to DHT. In people with a genetic sensitivity, DHT miniaturizes hair follicles and causes hair loss and baldness.
Men and women with androgenetic alopecia are sensitive to the effects of DHT on the hair follicle. Reducing DHT slows hair loss and promotes hair growth.
Ask your Invigor Medical treatment specialist or doctor about alternatives to minoxidil, especially if you are concerned about potential side effects. Your Invigor Medical specialist can discuss hair loss treatment options as part of your age-management treatment plan.










